Rafaffaffaagagag
ROI Maximizer
LEVEL 1
200 XP
In this tutorial we will create a Simple File Upload With Django. Django is a free and open source web application framework, written in Python. The official project site describes Django as "a high-level Python Web framework that encourages rapid development and clean, pragmatic design. So let's now do the coding...
Getting Started
First you will have to download & install the Python IDLE's, here's the link for the Integrated Development And Learning Environment for Python https://www.python.org/downloads/.
After Python IDLE's is installed, open the command prompt then type "pip install Django", and hit enter.
Wait for the django to be downloaded and installed at the same time. Then After that type "python -m django version" and hit enter to check if django is installed and what version of django is.
Creating the App
After setting django we will now create the web app for the web server. First create a new folder named "Django File Upload", then cd to a newly created folder, then type "django-admin startproject server" and hit enter. A new folder will be created on the directory named 'server'.
Running The Server
After creating a project, cd to the newly created directory, then type "manage.py runserver" and hit enter to start the server running. The "manage.py" is a command of django-admin that utilize the administrative tasks of python web framework.
Here is the image of python web server:
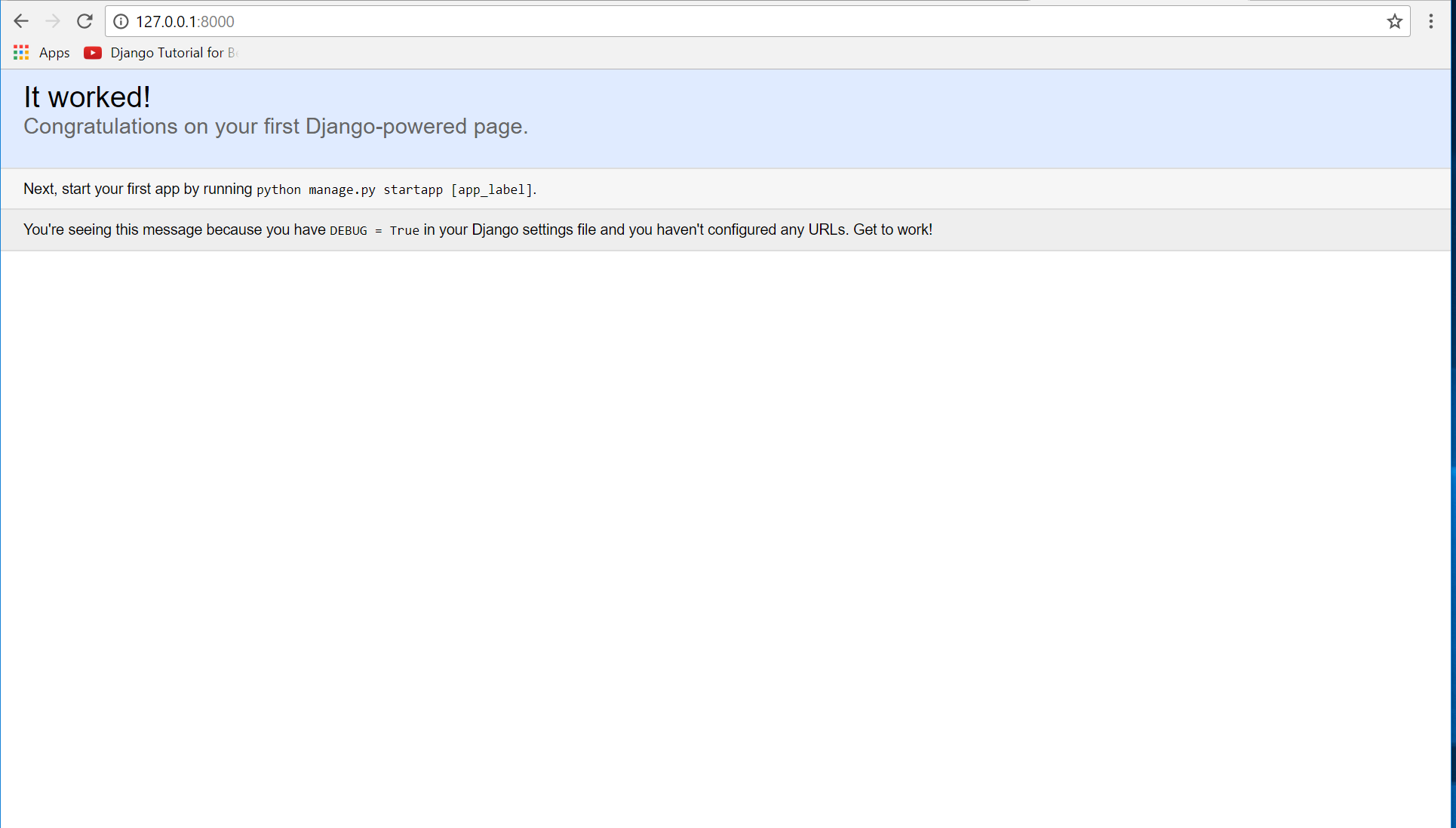
Note: Type '127.0.0.1:8000' in the url browser to view the server. When there is code changes in the server just (ctrl + C) to command prompt to stop the server from running, then start again to avoid errors.
Creating The Website
This time will now create the web app to display the web models. First locate the directory of the app via command prompt cd, then type "manage.py startapp file" and hit enter. A new directory will be create inside the app named "file".
Setting up The URL
This time will now create a url address to connect the app from the server. First Go to server directory, then open urls via Python IDLE's or any text editor. Then import "include" module beside the url module and import additional module to make a redirect url to your site "from . import views". After that copy/paste the code below inside the urlpatterns.
Then import two modules called:
After that create a statement to access the media root
It will be look like this:
Then after that create a view that will catch the redirect url. To do that create a file "views.py" then copy/paste the code below and save it as "views.py".
Creating The Path For The Pages
Now that we set the connect we will now create a path for the web pages. All you have to do first is to go to file directory, then copy/paste the code below and save it inside "file" directory named 'urls.py' The file name must be urls.py or else there will be an error in the code.
Creating A Static Folder
This time we will create a directory that store an external file. First go to the file directory then create a directory called "static", after that create a sub directory called "file". You'll notice that it is the same as your main app directory name, to assure the absolute link. This is where you import the css, js, etc directory.
Creating The Views
The views contains the interface of the website. This is where you assign the html code for rendering it to django framework and contains a methods that call a specific functions. To do that first open the views.py, the copy/paste the code below.
Registering The App To The Server
Now that we created the interface we will now then register the app to the server. To do that go to the server directory, then open "settings.py" via Python IDLE's or any text editor. Then copy/paste this script inside the INSTALLED_APP variables 'file'.
It will be like this:
Then we will create an absolute link that give access to MEDIA root folder, copy the code below then paste it below the STATIC_URL
Creating The Mark up Language
Now we will create the html interface for the django framework. First go to file directory, then create a directory called "templates" and create a sub directory on it called file.
base.html
Save it as "base.html" inside the file directory "sub directory of templates".
index.html
Save it as "index.html" inside the file directory "sub directory of templates".
Migrating The App To The Server
Now that we done in setting up all the necessary needed, we will now then make a migration and migrate the app to the server at the same time. To do that open the command prompt then cd to the "server" directory, then type "manage.py makemigrations" and hit enter. After that type again "manage.py migrate" then hit enter.
Now try to run the server again, and see if all things are done.
There you have it we successfully created a Simple File Upload With Django. I hope that this simple tutorial help you for what you are looking for. For more updates and tutorials just kindly visit this site. Enjoy Coding!!!
Download
Getting Started
First you will have to download & install the Python IDLE's, here's the link for the Integrated Development And Learning Environment for Python https://www.python.org/downloads/.
After Python IDLE's is installed, open the command prompt then type "pip install Django", and hit enter.

Wait for the django to be downloaded and installed at the same time. Then After that type "python -m django version" and hit enter to check if django is installed and what version of django is.

Creating the App
After setting django we will now create the web app for the web server. First create a new folder named "Django File Upload", then cd to a newly created folder, then type "django-admin startproject server" and hit enter. A new folder will be created on the directory named 'server'.

Running The Server
After creating a project, cd to the newly created directory, then type "manage.py runserver" and hit enter to start the server running. The "manage.py" is a command of django-admin that utilize the administrative tasks of python web framework.
Here is the image of python web server:

Note: Type '127.0.0.1:8000' in the url browser to view the server. When there is code changes in the server just (ctrl + C) to command prompt to stop the server from running, then start again to avoid errors.
Creating The Website
This time will now create the web app to display the web models. First locate the directory of the app via command prompt cd, then type "manage.py startapp file" and hit enter. A new directory will be create inside the app named "file".

Setting up The URL
This time will now create a url address to connect the app from the server. First Go to server directory, then open urls via Python IDLE's or any text editor. Then import "include" module beside the url module and import additional module to make a redirect url to your site "from . import views". After that copy/paste the code below inside the urlpatterns.
- url(
r'^$'
,
views.index_redirect
,
name=
'views_redirect'
)
,
- url(
r'^file/$'
,
include(
'file.urls'
)
)
,
Then import two modules called:
- from
django.conf
import
settings
- from
django.conf
.urls
.static
import
static
After that create a statement to access the media root
- if
settings.DEBUG
:
- urlpatterns +=
static(
settings.STATIC_URL
,
document_root=
settings.STATIC_ROOT
)
- urlpatterns +=
static(
settings.MEDIA_URL
,
document_root=
settings.MEDIA_ROOT
)
It will be look like this:
- from
django.conf
.urls
import
include,
url
- from
django.contrib
import
admin
- from
django.conf
import
settings
- from
django.conf
.urls
.static
import
static
- from
. import
views
- urlpatterns =
[
- url(
r'^$'
,
views.index_redirect
,
name=
'views_redirect'
)
,
- url(
r'^file/'
,
include(
'file.urls'
)
)
,
- url(
r'^admin/'
,
admin.site
.urls
)
,
- ]
- if
settings.DEBUG
:
- urlpatterns +=
static(
settings.STATIC_URL
,
document_root=
settings.STATIC_ROOT
)
- urlpatterns +=
static(
settings.MEDIA_URL
,
document_root=
settings.MEDIA_ROOT
)
Then after that create a view that will catch the redirect url. To do that create a file "views.py" then copy/paste the code below and save it as "views.py".
- from
django.shortcuts
import
redirect
- def
index_redirect(
request)
:
- return
redirect(
'/file/'
)
Creating The Path For The Pages
Now that we set the connect we will now create a path for the web pages. All you have to do first is to go to file directory, then copy/paste the code below and save it inside "file" directory named 'urls.py' The file name must be urls.py or else there will be an error in the code.
- from
django.conf
.urls
import
url
- from
. import
views
- urlpatterns =
[
- url(
r'^$'
,
views.index
,
name=
'index'
)
,
- ]
Creating A Static Folder
This time we will create a directory that store an external file. First go to the file directory then create a directory called "static", after that create a sub directory called "file". You'll notice that it is the same as your main app directory name, to assure the absolute link. This is where you import the css, js, etc directory.
Creating The Views
The views contains the interface of the website. This is where you assign the html code for rendering it to django framework and contains a methods that call a specific functions. To do that first open the views.py, the copy/paste the code below.
- from
django.shortcuts
import
render
- from
django.core
.files
.storage
import
FileSystemStorage
- from
.models
import
File
- import
os
,
datetime
- # Create your views here.
- def
index(
request)
:
- if
request.method
==
'POST'
and
request.FILES
[
'file'
]
:
- upload_file =
request.FILES
[
'file'
]
- extension =
os
.path
.splitext
(
upload_file.name
)
[
1
]
- rename =
datetime
.datetime
.now
(
)
.strftime
(
"%Y_%m_%d %H_%M_%S"
)
+ extension
- fss =
FileSystemStorage(
)
- filename =
fss.save
(
rename,
upload_file)
- file
=
File(
file
=
rename)
- file
.save
(
)
- upload_file_path =
fss.path
(
filename)
- return
render(
request,
'file/index.html'
,
{
- 'upload_file_path'
: upload_file_path
- }
)
- else
:
- return
render(
request,
'file/index.html'
)
Registering The App To The Server
Now that we created the interface we will now then register the app to the server. To do that go to the server directory, then open "settings.py" via Python IDLE's or any text editor. Then copy/paste this script inside the INSTALLED_APP variables 'file'.
It will be like this:
- INSTALLED_APPS =
[
- 'file'
,
- 'django.contrib.admin'
,
- 'django.contrib.auth'
,
- 'django.contrib.contenttypes'
,
- 'django.contrib.sessions'
,
- 'django.contrib.messages'
,
- 'django.contrib.staticfiles'
,
- ]
Then we will create an absolute link that give access to MEDIA root folder, copy the code below then paste it below the STATIC_URL
- MEDIA_ROOT =
os
.path
.join
(
BASE_DIR,
'media'
)
- MEDIA_URL =
'/media/'
Creating The Mark up Language
Now we will create the html interface for the django framework. First go to file directory, then create a directory called "templates" and create a sub directory on it called file.
base.html
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html
lang
=
"en"
>
- <head
>
- <meta
charset
=
"UTF-8"
name
=
"viewport"
content
=
"width=device-width, initial-scale=1"
/
>
- {% load static %}
- <link
rel
=
"stylesheet"
type
=
"text/css"
href
=
"{% static 'file/css/bootstrap.css' %}"
/
>
- </
head
>
- <body
>
- <nav class
=
"navbar navbar-default"
>
- <div
class
=
"container-fluid"
>
- <a
class
=
"navbar-brand"
href
=
"https://sourcecodster.com"
>
Sourcecodester</
a
>
- </
div
>
- </
nav>
- <div
class
=
"col-md-3"
></
div
>
- <div
class
=
"col-md-6 well"
>
- <h3
class
=
"text-primary"
>
Python - Simple File Upload With Django</
h3
>
- <hr
style
=
"border-top:1px dotted #000;"
/
>
- {% block body %}
- {% endblock %}
- </
div
>
- </
body
>
- </
html
>
Save it as "base.html" inside the file directory "sub directory of templates".
index.html
- {% extends 'file/base.html' %}
- {% block body %}
- <form
method
=
"POST"
enctype
=
"multipart/form-data"
>
- {% csrf_token %}
- <div
class
=
"form-group"
>
- <input
type
=
"file"
name
=
"file"
required=
"required"
/
>
- <br
/
>
- <button
type
=
"submit"
class
=
"btn btn-sm btn-primary"
><span
class
=
"glyphicon glyphicon-upload"
></
span
>
Upload</
button
>
- </
div
>
- </
form
>
- {% if upload_file_path %}
- Uploaded at: <label
class
=
"text-primary"
>
{{ upload_file_path }}</
label
>
- {% endif %}
- {% endblock %}
Save it as "index.html" inside the file directory "sub directory of templates".
Migrating The App To The Server
Now that we done in setting up all the necessary needed, we will now then make a migration and migrate the app to the server at the same time. To do that open the command prompt then cd to the "server" directory, then type "manage.py makemigrations" and hit enter. After that type again "manage.py migrate" then hit enter.

Now try to run the server again, and see if all things are done.
There you have it we successfully created a Simple File Upload With Django. I hope that this simple tutorial help you for what you are looking for. For more updates and tutorials just kindly visit this site. Enjoy Coding!!!
Download
You must upgrade your account or reply in the thread to view the hidden content.