AlvoErrado2
Tech Trends Analyst
2
MONTHS
2 2 MONTHS OF SERVICE
LEVEL 2
900 XP
In this article, we are going to study an important artifact of Windows, i.e. prefetch files. Every time you do anything on your Windows system, a file is created. These files are called Prefetch files. Through this article, we will learn how these are important and why do we need them.
Table of Content
Introduction
A Prefetch file is a file created when you open an application on your windows system. Windows makes a prefetch record when an application is run from a specific area for the absolute first time.
Prefetch files were introduced in Windows XP. Prefetch files are intended to accelerate the Windows boot process and applications’ start-up process. In Windows XP, Vista, and 7 the number of prefetch files is limited to 128 whereas in Windows 8 and above it is up to 1024.
Proof of program execution can be a significant asset for a forensic investigator, they can prove that a certain executable was executed on the system to cover up the tracks. Before initiating the forensic analysis of the prefetch record as a forensic examiner you should check whether the prefetching process is enabled.
To check the status of prefetching, open the following location in Registry editor:
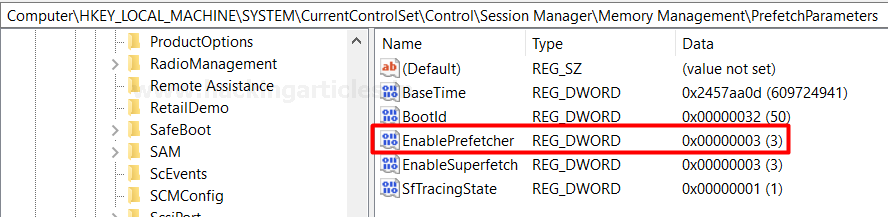
The value is set as 3 by default as shown in the image above. The following values can be changed according to your prefetching needs. All the options that windows provide us with in order to customize prefetching are explained below:
The metadata that can be found in a single prefetch file is as following:
The prefetch files are saved under %SystemRoot%\Prefetch (C:\Windows\Prefetch).

You can open the prefetch files location you can directly search for “prefetch “in the run command.

It can also be opened as a directory from the command prompt, which is a good news for all the command-line lovers.

Forensic Analysis of Prefetch Files
WinPrefetch View
WinPrefetch View is a tool to read and examine the prefetch files stored in your system. The tool was developed by Nirsoft. This utility deals with any variant of Windows, beginning from Windows XP to Windows 10.
You can download the tool from here.

You can easily open the details of a particular prefetch file by simply clicking on it. Here, I have opened HFS.EXE-D3CAF0BF.pf for a detailed view. It shows details such as created time, modified time, file size, the path of process run count, last run time, missing process.

OS Forensics
OS Forensic is a digital forensic tool, a complete package for forensic investigation by Passmark software. It is used to extract, analyze data, search files, recover deleted passwords, and recover deleted evidence, much more.
Download the tool from here.

Prefetch Explorer Command Line (PECmd)
PECmd is a command-line tool by Eric Zimmerman, used for bulk analysis of prefetch files.This tool can also export your prefetch artifacts to .csv and .css.
You can download the tool from here.
To begin with run the executable file. Let’s parse the prefetch file using this tool we will use the –d parameter to parse all the prefetch file.

In the image below, you can see the prefetch file for firefox.exe.The tool has parsed all the metadata as it has been explained in the introduction.

Similarly, through the following image, you can observe the prefetch file forHFS.exe. Such files will be created for every application you access.

FTK Imager
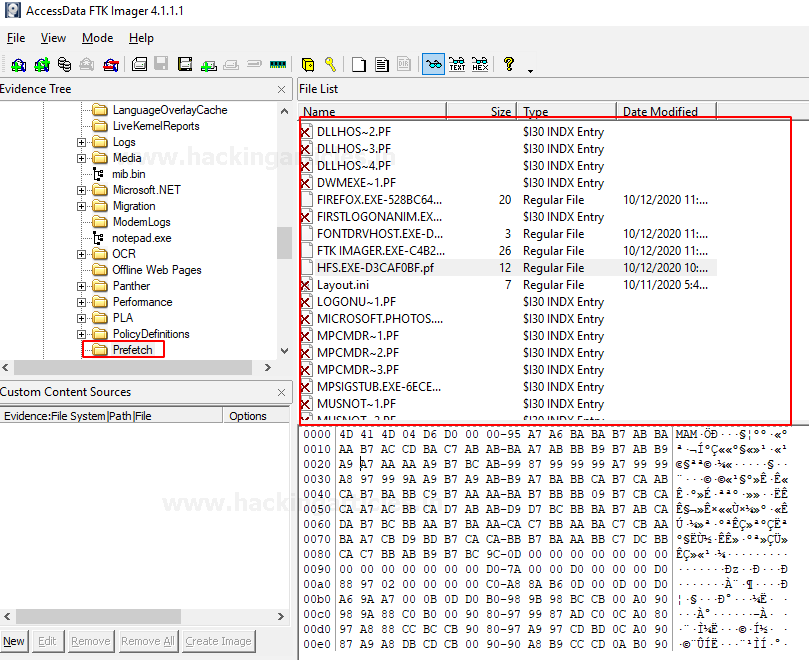
As a Forensic Investigator, you can always access the prefetch files to understand the case given to you. Because through these files, it can be determined that what was frequently used on the system that you are investigating. This can be easily done with FTK Imager. FTK imager allows one to view and analyze the prefetch file present in the drive. To access the prefetch file through FTK, just open the said tool and look for the Prefetch folder in the left panel as highlighted in the image below:
This is all on prefetch files. Now that we understand these files properly, we can customize it, access it, and use it as we need. The most important thing to know about prefetch files is that it a boon when comes to retracing a malware as any .exe file that has been run on the system, will be logged in prefetch files. Therefore, if a malicious file is executed; you can track it through this.
Author: Vishva Vaghela is a Digital Forensics enthusiast and enjoys technical content writing. You can reach her on Here
Table of Content
- Introduction
- Forensic Analysis of Prefetch Files
- WinPrefetch View
- OS Forensic
- PECmd
- FTK Imager
Introduction
A Prefetch file is a file created when you open an application on your windows system. Windows makes a prefetch record when an application is run from a specific area for the absolute first time.
Prefetch files were introduced in Windows XP. Prefetch files are intended to accelerate the Windows boot process and applications’ start-up process. In Windows XP, Vista, and 7 the number of prefetch files is limited to 128 whereas in Windows 8 and above it is up to 1024.
Proof of program execution can be a significant asset for a forensic investigator, they can prove that a certain executable was executed on the system to cover up the tracks. Before initiating the forensic analysis of the prefetch record as a forensic examiner you should check whether the prefetching process is enabled.
To check the status of prefetching, open the following location in Registry editor:
Code:
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Memory Management\PrefetchParameters
The value is set as 3 by default as shown in the image above. The following values can be changed according to your prefetching needs. All the options that windows provide us with in order to customize prefetching are explained below:
- 0:Prefetching Disabled
- 1:Application Prefetching Enabled
- 2: Boot Prefetching Enabled
- 3:Application and Boot both Enabled
The metadata that can be found in a single prefetch file is as following:
- Executable’s name
- Eight character hash of the executable path.
- The path of the executable file
- Creation, modified, and accessed timestamp of executable
- Run count (Number of time the application has been executed)
- Last run time
- The timestamp for the last 8 run time (1 last run time and other 7 other last run times)
- Volume information
- File Referenced by the executable
- Directories referenced by the executable
The prefetch files are saved under %SystemRoot%\Prefetch (C:\Windows\Prefetch).

You can open the prefetch files location you can directly search for “prefetch “in the run command.

It can also be opened as a directory from the command prompt, which is a good news for all the command-line lovers.

Forensic Analysis of Prefetch Files
WinPrefetch View
WinPrefetch View is a tool to read and examine the prefetch files stored in your system. The tool was developed by Nirsoft. This utility deals with any variant of Windows, beginning from Windows XP to Windows 10.
You can download the tool from here.

You can easily open the details of a particular prefetch file by simply clicking on it. Here, I have opened HFS.EXE-D3CAF0BF.pf for a detailed view. It shows details such as created time, modified time, file size, the path of process run count, last run time, missing process.

OS Forensics
OS Forensic is a digital forensic tool, a complete package for forensic investigation by Passmark software. It is used to extract, analyze data, search files, recover deleted passwords, and recover deleted evidence, much more.
Download the tool from here.

Prefetch Explorer Command Line (PECmd)
PECmd is a command-line tool by Eric Zimmerman, used for bulk analysis of prefetch files.This tool can also export your prefetch artifacts to .csv and .css.
You can download the tool from here.
To begin with run the executable file. Let’s parse the prefetch file using this tool we will use the –d parameter to parse all the prefetch file.
Code:
PECmd.exe –d "C:\Windows\Prefetch"
In the image below, you can see the prefetch file for firefox.exe.The tool has parsed all the metadata as it has been explained in the introduction.

Similarly, through the following image, you can observe the prefetch file forHFS.exe. Such files will be created for every application you access.

FTK Imager
As a Forensic Investigator, you can always access the prefetch files to understand the case given to you. Because through these files, it can be determined that what was frequently used on the system that you are investigating. This can be easily done with FTK Imager. FTK imager allows one to view and analyze the prefetch file present in the drive. To access the prefetch file through FTK, just open the said tool and look for the Prefetch folder in the left panel as highlighted in the image below:
This is all on prefetch files. Now that we understand these files properly, we can customize it, access it, and use it as we need. The most important thing to know about prefetch files is that it a boon when comes to retracing a malware as any .exe file that has been run on the system, will be logged in prefetch files. Therefore, if a malicious file is executed; you can track it through this.

Author: Vishva Vaghela is a Digital Forensics enthusiast and enjoys technical content writing. You can reach her on Here