reprapdes1887
Test-Driven Developer
2
MONTHS
2 2 MONTHS OF SERVICE
LEVEL 1
300 XP
In this article you will read about the rules of the Sudoku game and the algorithm, used to solve the Sudoku puzzle.
In the next two articles I'll describe the complete step by step guide about how to implement a Sudoku puzzle game using MFC.
The goal of the Sudoku game is to fill the 9x9 grid with numbers from 1 to 9 in the next way:
Here is an example of the solved Sudoku:
The first step is to create the class that will represent the Sudoku puzzle. The definition of this class in my project is:
The constructor of the board is very simple. It just allocates memory for the arrays and calls generate(
)
function to generate the problem:
Before the description of the generate(
)
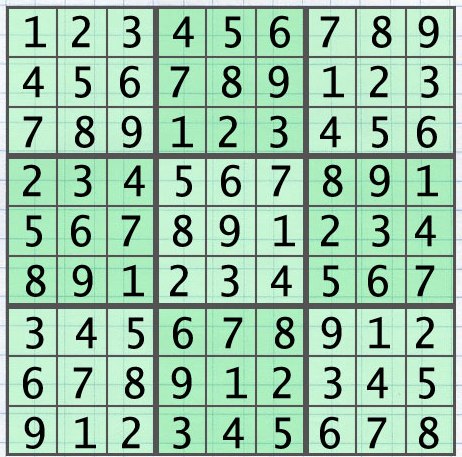
function I would like to describe the algorithm used by me. To generate a random puzzle I start from the "base grid" - a correct grid of Sudoku puzzle:
The next list of operations can be performed on the base grid and the rule of the Sudoku will be kept:
These transformations have next realization:
As you can see the swapping of the columns and columns sectors are done using already defined functions: transpose(
)
and swap_rows(
)
, swap_rows_sector(
)
;
The generation of the puzzle is done by random number of these transformations:
In this function we create a random already solved puzzle and save it's representation. After this we need to create a problem for the user: we need to erase some numbers from cells. It's done by createProblem(
)
function:
In this method numbers from the grid are randomly eliminated. After the cell is eliminated, the program checks if the problem can be resolved in a single way. If it can be resolved - number is deleted from cell. The check of the valid elimination is performed by the next functions:
These functions use the depth search algorithm with backtracking to find if any solution for the current state can be found.
As the result of generate(
)
function we have next things:
So, we have the full implementation of the Sudoku logic. In the next article I'll tell you how to create the interface of the Sudoku game.
In the next two articles I'll describe the complete step by step guide about how to implement a Sudoku puzzle game using MFC.
The goal of the Sudoku game is to fill the 9x9 grid with numbers from 1 to 9 in the next way:
- Each row contains all numbers from 1 to 9
- Each column contains all numbers from 1 to 9
- Each block of 3x3 cells contains all numbers from 1 to 9
Here is an example of the solved Sudoku:

The first step is to create the class that will represent the Sudoku puzzle. The definition of this class in my project is:
- #include "stdlib.h"
- #pragma once
- class
board
- {
- public
:
- int
difficulty;
//difficulty of the game
- board(
void
)
;
- ~board(
void
)
;
- int
**
numbers;
//array to store the current representation of the board
- int
**
solution;
//used to save the solution of the puzzle
- int
*
tempSol;
//temporary element
- void
generate(
)
;
//generate the random puzzle
- bool
checkNumberValidity(
int
,int
,int
)
;
- void
help(
)
;
//show help
- void
showSolution(
)
;
//show solution
- bool
win(
)
;
//check for winn
- private
:
- void
transpose(
)
;
//operations
- void
swap_rows(
)
;
//performed
- void
swap_columns(
)
;
//to generate
- void
swap_rows_sector(
)
;
//a new
- void
swap_columns_sector(
)
;
//puzzle
- void
createProblem(
)
;
- bool
solve(
)
;
- void
placeNumber(
int
)
;
- bool
checkValidity(
int
,int
,int
)
;
- }
;
The constructor of the board is very simple. It just allocates memory for the arrays and calls generate(
)
function to generate the problem:
- board::
board
(
void
)
- {
- difficulty =
30
;
- numbers =
new
int
*
[
9
]
;
- solution =
new
int
*
[
9
]
;
- tempSol =
new
int
[
81
]
;
- for
(
int
i =
0
;
i!
=
9
;
++
i)
- {
- numbers[
i]
=
new
int
[
9
]
;
- solution[
i]
=
new
int
[
9
]
;
- }
- generate(
)
;
- }
Before the description of the generate(
)
function I would like to describe the algorithm used by me. To generate a random puzzle I start from the "base grid" - a correct grid of Sudoku puzzle:

The next list of operations can be performed on the base grid and the rule of the Sudoku will be kept:
- transpose grid
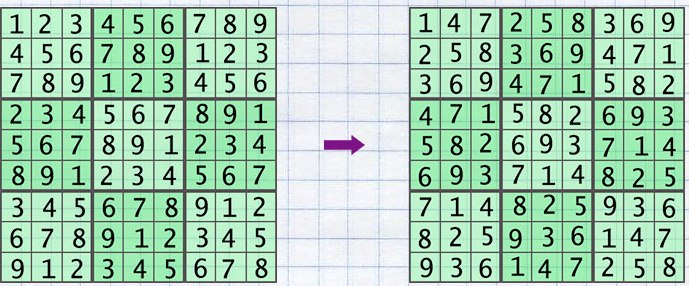
- swap 2 rows
- swap 2 columns
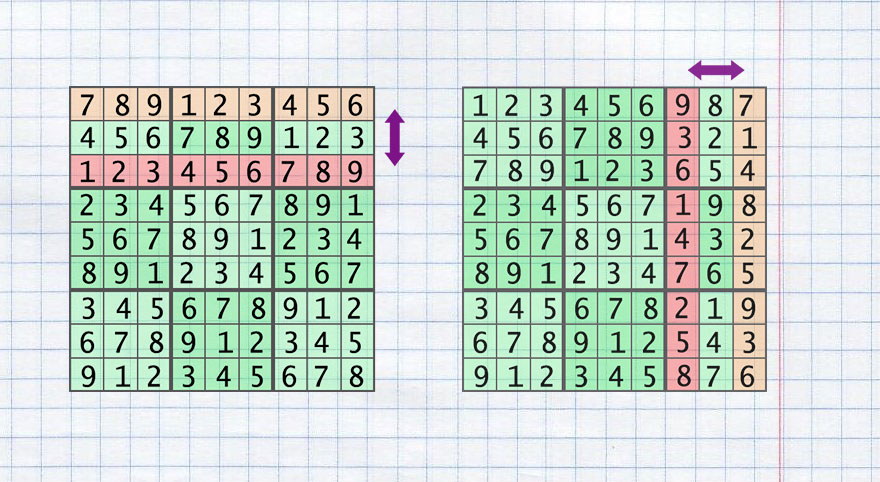
- swap 2 sectors of rows
- swap 2 sectors columns
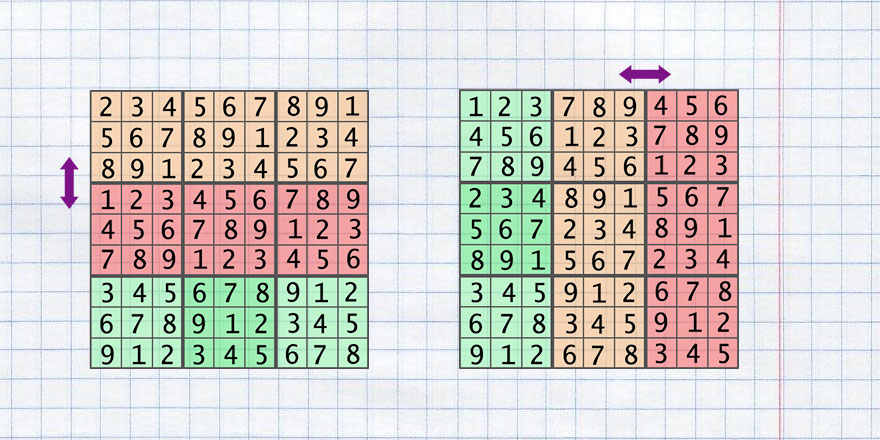
These transformations have next realization:
- void
board::
swap_rows
(
)
- {
- srand
(
time
(
NULL
)
)
;
- int
sector =
rand
(
)
%
3
;
- int
row_number1 =
rand
(
)
%
3
;
- int
row_number2;
- do
- row_number2 =
rand
(
)
%
3
;
- while
(
row_number1 ==
row_number2)
;
- for
(
int
i =
0
;
i !
=
9
;
++
i)
- {
- int
temp =
numbers[
sector*
3
+
row_number2]
[
i]
;
- numbers[
sector*
3
+
row_number2]
[
i]
=
numbers[
sector*
3
+
row_number1]
[
i]
;
- numbers[
sector*
3
+
row_number1]
[
i]
=
temp;
- }
- }
- void
board::
swap_columns
(
)
- {
- transpose(
)
;
- swap_rows(
)
;
- transpose(
)
;
- }
- void
board::
transpose
(
)
- {
- int
**
temp;
- temp =
new
int
*
[
9
]
;
- for
(
int
i =
0
;
i !
=
9
;
++
i)
- temp[
i]
=
new
int
[
9
]
;
- for
(
int
i =
0
;
i !
=
9
;
++
i)
- for
(
int
j =
0
;
j !
=
9
;
++
j)
- temp[
i]
[
j]
=
numbers[
j]
[
i]
;
- for
(
int
i =
0
;
i !
=
9
;
++
i)
- for
(
int
j =
0
;
j!
=
9
;
++
j)
- numbers[
i]
[
j]
=
temp[
i]
[
j]
;
- }
- void
board::
swap_rows_sector
(
)
- {
- srand
(
time
(
NULL
)
)
;
- int
sector1 =
rand
(
)
%
3
;
- int
sector2;
- do
- sector2 =
rand
(
)
%
3
;
- while
(
sector1 ==
sector2)
;
- for
(
int
i =
0
;
i !
=
3
;
++
i)
- {
- for
(
int
j =
0
;
j !
=
9
;
++
j)
- {
- int
temp =
numbers[
sector2*
3
+
i]
[
j]
;
- numbers[
sector2*
3
+
i]
[
j]
=
numbers[
sector1*
3
+
i]
[
j]
;
- numbers[
sector1*
3
+
i]
[
j]
=
temp;
- }
- }
- }
- void
board::
swap_columns_sector
(
)
- {
- transpose(
)
;
- swap_rows_sector(
)
;
- transpose(
)
;
- }
As you can see the swapping of the columns and columns sectors are done using already defined functions: transpose(
)
and swap_rows(
)
, swap_rows_sector(
)
;
The generation of the puzzle is done by random number of these transformations:
- void
board::
generate
(
)
- {
- for
(
int
i1 =
0
,k =
0
;
i1 !
=
9
;
++
i1,k +
=
3
)
{
- for
(
int
i2 =
0
;
i2 !
=
9
;
++
i2,k++
)
{
- numbers[
i1]
[
i2]
=
k%
9
+
1
;
- }
- if
(
i1==
2
)
- k++
;
- if
(
i1 ==
5
)
- k++
;
- }
- srand
(
time
(
NULL
)
)
;
- for
(
int
i =
0
;
i !
=
100
;
++
i)
- {
- switch
(
rand
(
)
%
5
)
- {
- case
0
:
transpose(
)
;
- break
;
- case
1
:
swap_rows(
)
;
- break
;
- case
2
:
swap_columns(
)
;
- break
;
- case
3
:
swap_rows_sector(
)
;
- break
;
- case
4
:
swap_columns_sector(
)
;
- break
;
- }
- }
- for
(
int
i =
0
;
i !
=
9
;
++
i)
- for
(
int
j =
0
;
j !
=
9
;
++
j)
- solution[
i]
[
j]
=
numbers[
i]
[
j]
;
- for
(
int
i =
0
;
i !
=
9
;
++
i)
{
- for
(
int
j =
0
;
j !
=
9
;
++
j)
- tempSol[
i*
9
+
j]
=
numbers[
i]
[
j]
;
- }
- createProblem(
)
;
- }
In this function we create a random already solved puzzle and save it's representation. After this we need to create a problem for the user: we need to erase some numbers from cells. It's done by createProblem(
)
function:
- void
board::
createProblem
(
)
- {
- for
(
int
k =
0
;
k !
=
difficulty;
)
- {
- int
i;
- int
j;
- do
- {
- i =
rand
(
)
%
9
;
- j =
rand
(
)
%
9
;
- }
- while
(
numbers[
i]
[
j]
==
0
)
;
- int
save =
numbers[
i]
[
j]
;
- numbers[
i]
[
j]
=
0
;
- tempSol[
i*
9
+
j]
=
0
;
- if
(
!
solve(
)
)
- {
- numbers[
i]
[
j]
=
save;
- tempSol[
i*
9
+
j]
=
save;
- }
- else
- ++
k;
- }
- }
In this method numbers from the grid are randomly eliminated. After the cell is eliminated, the program checks if the problem can be resolved in a single way. If it can be resolved - number is deleted from cell. The check of the valid elimination is performed by the next functions:
- bool
board::
solve
(
)
- {
- try
{
- placeNumber(
0
)
;
- return
false
;
- }
catch
(
char
*
ex)
{
- return
true
;
- }
- }
- void
board::
placeNumber
(
int
position)
- {
- if
(
position==
81
)
- throw
(
char
*
)
"Finished!"
;
- if
(
tempSol[
position]
)
- {
- placeNumber(
position+
1
)
;
- return
;
- }
- for
(
int
n =
1
;
n!
=
10
;
++
n)
- {
- if
(
checkValidity(
n,position%
9
, position /
9
)
)
- {
- tempSol[
position]
=
n;
- placeNumber(
position+
1
)
;
- tempSol[
position]
=
0
;
- }
- }
- }
- bool
board::
checkValidity
(
int
value, int
x, int
y)
- {
- for
(
int
i =
0
;
i !
=
9
;
++
i)
- {
- if
(
tempSol[
y*
9
+
i]
==
value ||
tempSol[
i*
9
+
x]
==
value)
- return
false
;
- }
- int
startX =
(
x /
3
)
*
3
;
- int
startY =
(
y /
3
)
*
3
;
- for
(
int
i =
startY;
i <
startY +
3
;
i++
)
{
- for
(
int
j =
startX;
j <
startX +
3
;
j++
)
{
- if
(
tempSol[
i *
9
+
j]
==
value)
- return
false
;
- }
- }
- return
true
;
- }
- bool
board::
checkNumberValidity
(
int
value, int
x, int
y)
- {
- for
(
int
i =
0
;
i !
=
9
;
++
i)
- {
- if
(
numbers[
x]
[
i]
==
value ||
numbers[
i]
[
y]
==
value)
- return
false
;
- }
- int
startX =
(
x /
3
)
*
3
;
- int
startY =
(
y /
3
)
*
3
;
- for
(
int
i =
startY;
i <
startY +
3
;
i++
)
{
- for
(
int
j =
startX;
j <
startX +
3
;
j++
)
{
- if
(
numbers[
j]
[
i]
==
value)
- return
false
;
- }
- }
- return
true
;
- }
These functions use the depth search algorithm with backtracking to find if any solution for the current state can be found.
As the result of generate(
)
function we have next things:
- A grid that represents the solution of the Sudoku puzzle
- A grid a copy of the solution but without some numbers in cells
So, we have the full implementation of the Sudoku logic. In the next article I'll tell you how to create the interface of the Sudoku game.